The wife loses a stone; the husband blames the wife; the wife blames the jeweler; the jeweler blames the manufacturer; the manufacturer looks for an answer. You want an answer to the question.
What causes most prong breakage? Chlorine and bromine.
Where does it come from? Hot tubs, swimming pools and laundry products.
Chlorine and bromine are commonly used chemical products to prevent bacteria from growing in our drinking water, in swimming pools and hot tubs. Too much of these compounds added may cause a human health threat and a durability problem for settings. The higher the concentration, the longer the exposure, and the higher the temperature all lead to a faster deterioration of the metal setting.
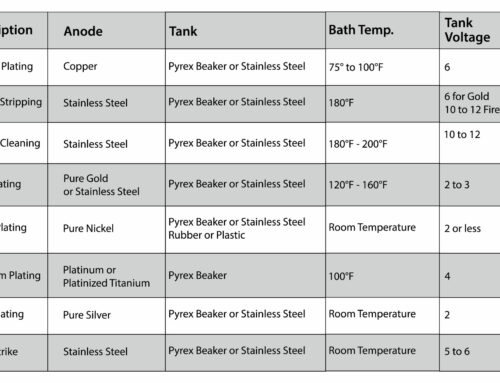
A controlled experiment was done to determine the effect of common chlorine and bromine products on jewelry settings. The tests were done with household bleach (heated and unheated), hot tub chlorine, bromine solutions, and a chlorine free dish washing detergent. The tests were done on 14K and 18K nickel white gold settings: set and unset, rhodium plated and not plated; palladium white gold and platinum settings.
The testing on the products was rated from most durable to the least durable as follows: Platinum, rhodium plated 14K palladium white gold, 14K palladium white gold, rhodium plated nickel white gold, 18K nickel white gold; and 14K nickel white gold.
The test solutions are listed in order from the product causing the most damage to the least harmful.
The rings soaked in heated bleach suffered the most catastrophic failure. The 14K nickel white gold was the first to fail in all solutions except the household detergent. The household detergent had little or no effect on the rings or settings. The test was stopped when the first setting failed and all items were compared.
Results of Each Solution
Based on our testing, a consumer wearing a 14K nickel white gold setting would lose a stone or expect prong breakage as follows:
- Using a 5% chlorine bleach heated to 110 degrees F°, prong failure would occur after 21 hours of exposure. Only the platinum and palladium white gold settings held their stones in the worst test solution.
- Using a 5% chlorine bleach at room temperature, prong failure would occur after 120 hours of exposure.
- With 5 ppm (parts per million) chlorine using hot tub chemicals, prong failure would occur after 312 hours or 156 days * based on 2 hours a day, 7 days a week.
- With 5 ppm (parts per million) bromine using hot tub chemicals, prong failure would occur after 384 hours or 192 days * based on 2 hours a day, 7 days a week.
- Household detergent would have no visible effects on the setting.
Recommendations
Use platinum settings or 14K palladium white settings. Rhodium plating will provide a protective coating to protect the setting; similar to paint stopping rust.
Customers should be warned not to wear their jewelry in hot tubs or swimming pools and told they must take jewelry off when using laundry or cleaning products. Never, never clean rings with bleach. Suggest that they bring them to a jeweler for cleaning and a checkup just like going to the dentist to have a teeth cleaning and check up.



Leave A Comment